| Properties | Methods |
Object
| Player version: | Flash Player 8 |
The use of filters depends on the object to which you apply the filter:
filters property. Setting the filters property of an object does not modify the object, and you can undo the filter by clearing the filters property. BitmapData.applyFilter() method. Calling applyFilter() on a BitmapData object takes the source BitmapData object and the filter object and generates a filtered image as a result.You can also apply filter effects to images and video during authoring. For more information, see your authoring documentation.
If you apply a filter to a movie clip or button, the cacheAsBitmap property of the movie clip or button is set to true. If you clear all filters, the original value of cacheAsBitmap is restored.
This filter supports Stage scaling. However, it does not support general scaling, rotation, and skewing; if the object itself is scaled (if _xscale and _yscale are not 100%), the filter effect is not scaled. It is scaled only when the Stage is zoomed.
A filter is not applied if the resulting image exceeds 2880 pixels in width or height. For example, if you zoom in on a large movie clip with a filter applied, the filter is turned off if the resulting image exceeds the limit of 2880 pixels.
See also| GradientGlowFilter.ratios, BitmapData.applyFilter(), Button.cacheAsBitmap, Button.filters, GlowFilter class, MovieClip.cacheAsBitmap, MovieClip.filters, TextField.filters |
| Property Summary | |
| alphas : Array
An array of alpha transparency values for the corresponding colors in the colors array. |
| angle : Number
The angle, in degrees. |
| blurX : Number
The amount of horizontal blur. |
| blurY : Number
The amount of vertical blur. |
| colors : Array
An array of colors that defines a gradient. |
| distance : Number
The offset distance of the glow. |
| knockout : Boolean
Specifies whether the object has a knockout effect. |
| quality : Number
The number of times to apply the filter. |
| ratios : Array
An array of color distribution ratios for the corresponding colors in the colors array. |
| strength : Number
The strength of the imprint or spread. |
| type : String
The placement of the filter effect. |
| Properties inherited from class Object |
__proto__, __resolve, constructor, prototype |
| Constructor Summary | |
GradientGlowFilter([distance:Number], [angle:Number], [colors:Array], [alphas:Array], [ratios:Array], [blurX:Number], [blurY:Number], [strength:Number], [quality:Number], [type:String], [knockout:Boolean])
Initializes the filter with the specified parameters. |
|
| Method Summary | |
| clone() : GradientGlowFilter
Returns a copy of this filter object. |
| Methods inherited from class BitmapFilter |
clone |
| Methods inherited from class Object |
addProperty, hasOwnProperty, isPropertyEnumerable, isPrototypeOf, registerClass, toString, unwatch, valueOf, watch |
| Property Detail |
public alphas : Array
| Player version: | Flash Player 8 |
colors array. Valid values for each element in the array are 0 to 1. For example, .25 sets the alpha transparency value to 25%. The alphas property cannot be changed by directly modifying its values. Instead, you must get a reference to alphas, make the change to the reference, and then set alphas to the reference.
The colors, alphas, and ratios properties are all related. The first element in the colors array corresponds to the first element in the alphas array and in the ratios array, and so on.
alphas property on an existing movie clip when a user clicks it.
import flash.filters.GradientGlowFilter;
var mc:MovieClip = createGradientGlowRectangle("GlowAlphas");
mc.onRelease = function() {
var filter:GradientGlowFilter = this.filters[0];
var alphas:Array = filter.alphas;
alphas.pop();
alphas.pop();
alphas.push(.3);
alphas.push(1);
filter.alphas = alphas;
this.filters = new Array(filter);
}
function createGradientGlowRectangle(name:String):MovieClip {
var art:MovieClip = this.createEmptyMovieClip(name, this.getNextHighestDepth());
var w:Number = 100;
var h:Number = 100;
art.beginFill(0x003366);
art.lineTo(w, 0);
art.lineTo(w, h);
art.lineTo(0, h);
art.lineTo(0, 0);
art._x = 20;
art._y = 20;
var colors:Array = [0xFFFFFF, 0xFF0000, 0xFFFF00, 0x00CCFF];
var alphas:Array = [0, 1, 1, 1];
var ratios:Array = [0, 63, 126, 255];
var filter:GradientGlowFilter = new GradientGlowFilter(0, 45, colors, alphas, ratios, 55, 55, 2.5, 2, "outer", false);
var filterArray:Array = new Array();
filterArray.push(filter);
art.filters = filterArray;
return art;
}
| GradientGlowFilter.colors, GradientGlowFilter.ratios |
public angle : Number
| Player version: | Flash Player 8 |
The angle value represents the angle of the theoretical light source falling on the object and determines the placement of the effect relative to the object. If distance is set to 0, the effect is not offset from the object, and therefore the angle property has no effect.
angle property on an existing movie clip when a user clicks it.
import flash.filters.GradientGlowFilter;
var mc:MovieClip = createGradientGlowRectangle("GlowAngle");
mc.onRelease = function() {
var filter:GradientGlowFilter = this.filters[0];
filter.distance = 50;
filter.angle = 90;
this.filters = new Array(filter);
}
function createGradientGlowRectangle(name:String):MovieClip {
var art:MovieClip = this.createEmptyMovieClip(name, this.getNextHighestDepth());
var w:Number = 100;
var h:Number = 100;
art.beginFill(0x003366);
art.lineTo(w, 0);
art.lineTo(w, h);
art.lineTo(0, h);
art.lineTo(0, 0);
art._x = 20;
art._y = 20;
var colors:Array = [0xFFFFFF, 0xFF0000, 0xFFFF00, 0x00CCFF];
var alphas:Array = [0, 1, 1, 1];
var ratios:Array = [0, 63, 126, 255];
var filter:GradientGlowFilter = new GradientGlowFilter(0, 45, colors, alphas, ratios, 55, 55, 2.5, 2, "outer", false);
var filterArray:Array = new Array();
filterArray.push(filter);
art.filters = filterArray;
return art;
}
public blurX : Number
| Player version: | Flash Player 8 |
blurX property on an existing movie clip when a user clicks it.
import flash.filters.GradientGlowFilter;
var mc:MovieClip = createGradientGlowRectangle("GlowBlurX");
mc.onRelease = function() {
var filter:GradientGlowFilter = this.filters[0];
filter.blurX = 255;
this.filters = new Array(filter);
}
function createGradientGlowRectangle(name:String):MovieClip {
var art:MovieClip = this.createEmptyMovieClip(name, this.getNextHighestDepth());
var w:Number = 100;
var h:Number = 100;
art.beginFill(0x003366);
art.lineTo(w, 0);
art.lineTo(w, h);
art.lineTo(0, h);
art.lineTo(0, 0);
art._x = 20;
art._y = 20;
var colors:Array = [0xFFFFFF, 0xFF0000, 0xFFFF00, 0x00CCFF];
var alphas:Array = [0, 1, 1, 1];
var ratios:Array = [0, 63, 126, 255];
var filter:GradientGlowFilter = new GradientGlowFilter(0, 45, colors, alphas, ratios, 55, 55, 2.5, 2, "outer", false);
var filterArray:Array = new Array();
filterArray.push(filter);
art.filters = filterArray;
return art;
}
public blurY : Number
| Player version: | Flash Player 8 |
blurY property on an existing movie clip when a user clicks it.
import flash.filters.GradientGlowFilter;
var mc:MovieClip = createGradientGlowRectangle("GlowBlurY");
mc.onRelease = function() {
var filter:GradientGlowFilter = this.filters[0];
filter.blurY = 255;
this.filters = new Array(filter);
}
function createGradientGlowRectangle(name:String):MovieClip {
var art:MovieClip = this.createEmptyMovieClip(name, this.getNextHighestDepth());
var w:Number = 100;
var h:Number = 100;
art.beginFill(0x003366);
art.lineTo(w, 0);
art.lineTo(w, h);
art.lineTo(0, h);
art.lineTo(0, 0);
art._x = 20;
art._y = 20;
var colors:Array = [0xFFFFFF, 0xFF0000, 0xFFFF00, 0x00CCFF];
var alphas:Array = [0, 1, 1, 1];
var ratios:Array = [0, 63, 126, 255];
var filter:GradientGlowFilter = new GradientGlowFilter(0, 45, colors, alphas, ratios, 55, 55, 2.5, 2, "outer", false);
var filterArray:Array = new Array();
filterArray.push(filter);
art.filters = filterArray;
return art;
}
public colors : Array
| Player version: | Flash Player 8 |
The colors property cannot be changed by directly modifying its values. Instead, you must get a reference to colors, make the change to the reference, and then set colors to the reference.
The colors, alphas, and ratios properties are all related. The first element in the colors array corresponds to the first element in the alphas array and in the ratios array, and so on.
colors property on an existing movie clip when a user clicks it.
import flash.filters.GradientGlowFilter;
var mc:MovieClip = createGradientGlowRectangle("GlowColors");
mc.onRelease = function() {
var filter:GradientGlowFilter = this.filters[0];
var colors:Array = filter.colors;
colors.pop();
colors.push(0xFF00FF);
filter.colors = colors;
this.filters = new Array(filter);
}
function createGradientGlowRectangle(name:String):MovieClip {
var art:MovieClip = this.createEmptyMovieClip(name, this.getNextHighestDepth());
var w:Number = 100;
var h:Number = 100;
art.beginFill(0x003366);
art.lineTo(w, 0);
art.lineTo(w, h);
art.lineTo(0, h);
art.lineTo(0, 0);
art._x = 20;
art._y = 20;
var colors:Array = [0xFFFFFF, 0xFF0000, 0xFFFF00, 0x00CCFF];
var alphas:Array = [0, 1, 1, 1];
var ratios:Array = [0, 63, 126, 255];
var filter:GradientGlowFilter = new GradientGlowFilter(0, 45, colors, alphas, ratios, 55, 55, 2.5, 2, "outer", false);
var filterArray:Array = new Array();
filterArray.push(filter);
art.filters = filterArray;
return art;
}
| GradientGlowFilter.alphas, GradientGlowFilter.ratios |
public distance : Number
| Player version: | Flash Player 8 |
distance property on an existing movie clip when a user clicks it.
import flash.filters.GradientGlowFilter;
var mc:MovieClip = createGradientGlowRectangle("GlowDistance");
mc.onRelease = function() {
var filter:GradientGlowFilter = this.filters[0];
filter.distance = 20;
this.filters = new Array(filter);
}
function createGradientGlowRectangle(name:String):MovieClip {
var art:MovieClip = this.createEmptyMovieClip(name, this.getNextHighestDepth());
var w:Number = 100;
var h:Number = 100;
art.beginFill(0x003366);
art.lineTo(w, 0);
art.lineTo(w, h);
art.lineTo(0, h);
art.lineTo(0, 0);
art._x = 20;
art._y = 20;
var colors:Array = [0xFFFFFF, 0xFF0000, 0xFFFF00, 0x00CCFF];
var alphas:Array = [0, 1, 1, 1];
var ratios:Array = [0, 63, 126, 255];
var filter:GradientGlowFilter = new GradientGlowFilter(0, 45, colors, alphas, ratios, 55, 55, 2.5, 2, "outer", false);
var filterArray:Array = new Array();
filterArray.push(filter);
art.filters = filterArray;
return art;
}
public knockout : Boolean
| Player version: | Flash Player 8 |
true specifies a knockout effect; the default is false (no knockout effect).
Example
knockout property on an existing movie clip when a user clicks it.
import flash.filters.GradientGlowFilter;
var mc:MovieClip = createGradientGlowRectangle("GlowKnockout");
mc.onRelease = function() {
var filter:GradientGlowFilter = this.filters[0];
filter.knockout = true;
this.filters = new Array(filter);
}
function createGradientGlowRectangle(name:String):MovieClip {
var art:MovieClip = this.createEmptyMovieClip(name, this.getNextHighestDepth());
var w:Number = 100;
var h:Number = 100;
art.beginFill(0x003366);
art.lineTo(w, 0);
art.lineTo(w, h);
art.lineTo(0, h);
art.lineTo(0, 0);
art._x = 20;
art._y = 20;
var colors:Array = [0xFFFFFF, 0xFF0000, 0xFFFF00, 0x00CCFF];
var alphas:Array = [0, 1, 1, 1];
var ratios:Array = [0, 63, 126, 255];
var filter:GradientGlowFilter = new GradientGlowFilter(0, 45, colors, alphas, ratios, 55, 55, 2.5, 2, "outer", false);
var filterArray:Array = new Array();
filterArray.push(filter);
art.filters = filterArray;
return art;
}
public quality : Number
| Player version: | Flash Player 8 |
For most applications, a quality value of 1, 2, or 3 is sufficient. Although you can use additional numeric values up to 15 to achieve different effects, higher values are rendered more slowly. Instead of increasing the value of quality, you can often get a similar effect, and with faster rendering, by simply increasing the values of blurX and blurY.
quality property on an existing movie clip when a user clicks it.
import flash.filters.GradientGlowFilter;
var mc:MovieClip = createGradientGlowRectangle("GlowQuality");
mc.onRelease = function() {
var filter:GradientGlowFilter = this.filters[0];
filter.quality = 3;
this.filters = new Array(filter);
}
function createGradientGlowRectangle(name:String):MovieClip {
var art:MovieClip = this.createEmptyMovieClip(name, this.getNextHighestDepth());
var w:Number = 100;
var h:Number = 100;
art.beginFill(0x003366);
art.lineTo(w, 0);
art.lineTo(w, h);
art.lineTo(0, h);
art.lineTo(0, 0);
art._x = 20;
art._y = 20;
var colors:Array = [0xFFFFFF, 0xFF0000, 0xFFFF00, 0x00CCFF];
var alphas:Array = [0, 1, 1, 1];
var ratios:Array = [0, 63, 126, 255];
var filter:GradientGlowFilter = new GradientGlowFilter(0, 45, colors, alphas, ratios, 55, 55, 2.5, 2, "outer", false);
var filterArray:Array = new Array();
filterArray.push(filter);
art.filters = filterArray;
return art;
}
public ratios : Array
| Player version: | Flash Player 8 |
colors array. Valid values are 0 to 255. The ratios property cannot be changed by directly modifying its values. Instead, you must get a reference to ratios, make the change to the reference, and then set ratios to the reference.
The colors, alphas, and ratios properties are all related. The first element in the colors array corresponds to the first element in the alphas array and in the ratios array, and so on.
Think of the gradient glow filter as a glow that emanates from the center of the object (if the distance value is set to 0), with gradients that are stripes of color blending into each other. The first color in the colors array is the outermost color of the glow. The last color is the innermost color of the glow.
Each value in the ratios array sets the position of the color on the radius of the gradient, where 0 represents the outermost point of the gradient and 255 represents the innermost point of the gradient. The ratio values can range from 0 to 255 pixels, in increasing value; for example [0, 64, 128, 200, 255]. Values from 0 to 128 appear on the outer edges of the glow. Values from 129 to 255 appear in the inner area of the glow. Depending on the ratio values of the colors and the type value of the filter, the filter colors might be obscured by the object to which the filter is applied.
In the following code and image, a filter is applied to a black circle movie clip, with the type set to "full". For instructional purposes, the first color in the colors array, pink, has an alpha value of 1, so it shows against the white document background. (In practice, you probably would not want the first color showing in this way.) Note the last color in the array, yellow, obscures the black circle to which the filter is applied:
var colors = [0xFFCCFF, 0x0000FF, 0x9900FF, 0xFF0000, 0xFFFF00];
var alphas = [1, 1, 1, 1, 1];
var ratios = [0, 32, 64, 128, 225];
var myGGF = new GradientGlowFilter(0, 0, colors, alphas, ratios, 50, 50, 1, 2, "full", false);
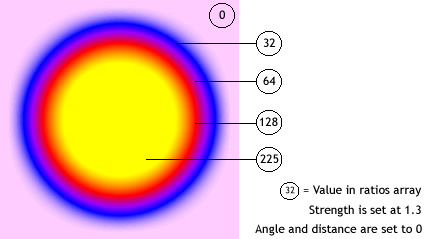
To achieve a seamless effect with your document background when you set the type value to "outer" or "full", set the first color in the array to the same color as the document background, or set the alpha value of the first color to 0; either technique makes the filter blend in with the background.
If you make two small changes in the code, the effect of the glow can be very different, even with the same ratios and colors arrays. Set the alpha value of the first color in the array to 0, to make the filter blend in with the document's white background; and set the type property to "outer" or "inner". Observe the results, as shown in the following images.
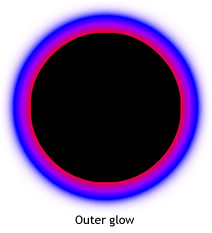
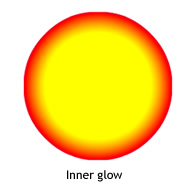
Keep in mind that the spread of the colors in the gradient varies based on the values of the blurX, blurY, strength, and quality properties, as well as the ratios values.
ratios property on an existing movie clip when a user clicks it.
import flash.filters.GradientGlowFilter;
var mc:MovieClip = createGradientGlowRectangle("GlowRatios");
mc.onRelease = function() {
var filter:GradientGlowFilter = this.filters[0];
var ratios:Array = filter.ratios;
ratios.shift();
ratios.unshift(40);
filter.ratios = ratios;
this.filters = new Array(filter);
}
function createGradientGlowRectangle(name:String):MovieClip {
var art:MovieClip = this.createEmptyMovieClip(name, this.getNextHighestDepth());
var w:Number = 100;
var h:Number = 100;
art.beginFill(0x003366);
art.lineTo(w, 0);
art.lineTo(w, h);
art.lineTo(0, h);
art.lineTo(0, 0);
art._x = 20;
art._y = 20;
var colors:Array = [0xFFFFFF, 0xFF0000, 0xFFFF00, 0x00CCFF];
var alphas:Array = [0, 1, 1, 1];
var ratios:Array = [0, 63, 126, 255];
var filter:GradientGlowFilter = new GradientGlowFilter(0, 45, colors, alphas, ratios, 55, 55, 2.5, 2, "outer", false);
var filterArray:Array = new Array();
filterArray.push(filter);
art.filters = filterArray;
return art;
}
| GradientGlowFilter.colors, GradientGlowFilter.alphas, MovieClip.beginGradientFill() |
public strength : Number
| Player version: | Flash Player 8 |
strength property on an existing movie clip when a user clicks it.
import flash.filters.GradientGlowFilter;
var mc:MovieClip = createGradientGlowRectangle("GlowStrength");
mc.onRelease = function() {
var filter:GradientGlowFilter = this.filters[0];
filter.strength = 1;
this.filters = new Array(filter);
}
function createGradientGlowRectangle(name:String):MovieClip {
var art:MovieClip = this.createEmptyMovieClip(name, this.getNextHighestDepth());
var w:Number = 100;
var h:Number = 100;
art.beginFill(0x003366);
art.lineTo(w, 0);
art.lineTo(w, h);
art.lineTo(0, h);
art.lineTo(0, 0);
art._x = 20;
art._y = 20;
var colors:Array = [0xFFFFFF, 0xFF0000, 0xFFFF00, 0x00CCFF];
var alphas:Array = [0, 1, 1, 1];
var ratios:Array = [0, 63, 126, 255];
var filter:GradientGlowFilter = new GradientGlowFilter(0, 45, colors, alphas, ratios, 55, 55, 2.5, 2, "outer", false);
var filterArray:Array = new Array();
filterArray.push(filter);
art.filters = filterArray;
return art;
}
public type : String
| Player version: | Flash Player 8 |
"outer": Glow on the outer edge of the object"inner": Glow on the inner edge of the object; the default"full": Glow on top of the objectThe default value is "inner".
type property on an existing movie clip when a user clicks it.
import flash.filters.GradientGlowFilter;
var mc:MovieClip = createGradientGlowRectangle("GlowType");
mc.onRelease = function() {
var filter:GradientGlowFilter = this.filters[0];
filter.type = "inner";
filter.strength = 1;
this.filters = new Array(filter);
}
function createGradientGlowRectangle(name:String):MovieClip {
var art:MovieClip = this.createEmptyMovieClip(name, this.getNextHighestDepth());
var w:Number = 100;
var h:Number = 100;
art.beginFill(0x003366);
art.lineTo(w, 0);
art.lineTo(w, h);
art.lineTo(0, h);
art.lineTo(0, 0);
art._x = 20;
art._y = 20;
var colors:Array = [0xFFFFFF, 0xFF0000, 0xFFFF00, 0x00CCFF];
var alphas:Array = [0, 1, 1, 1];
var ratios:Array = [0, 63, 126, 255];
var filter:GradientGlowFilter = new GradientGlowFilter(0, 45, colors, alphas, ratios, 55, 55, 2.5, 2, "outer", false);
var filterArray:Array = new Array();
filterArray.push(filter);
art.filters = filterArray;
return art;
}
| Constructor Detail |
public GradientGlowFilter([distance:Number], [angle:Number], [colors:Array], [alphas:Array], [ratios:Array], [blurX:Number], [blurY:Number], [strength:Number], [quality:Number], [type:String], [knockout:Boolean])
| Player version: | Flash Player 8 |
distance:Number [optional] — The offset distance of the glow. The default is 4. |
|
angle:Number [optional] — The angle, in degrees. Valid values are 0 to 360. The default is 45. |
|
colors:Array [optional] — An array of colors that defines a gradient. For example, red is 0xFF0000, blue is 0x0000FF, and so on. |
|
alphas:Array [optional] — An array of alpha transparency values for the corresponding colors in the colors array. Valid values for each element in the array are 0 to 1. For example, a value of .25 sets the alpha transparency value to 25%. |
|
ratios:Array [optional] — An array of color distribution ratios. Valid values are 0 to 255. This value defines the percentage of the width where the color is sampled at 100 percent. |
|
blurX:Number [optional] — The amount of horizontal blur. Valid values are 0 to 255. A blur of 1 or less means that the original image is copied as is. The default value is 4. Values that are a power of 2 (such as 2, 4, 8, 16 and 32) are optimized to render more quickly than other values. |
|
blurY:Number [optional] — The amount of vertical blur. Valid values are 0 to 255. A blur of 1 or less means that the original image is copied as is. The default value is 4. Values that are a power of 2 (such as 2, 4, 8, 16 and 32) are optimized to render more quickly than other values. |
|
strength:Number [optional] — The strength of the imprint or spread. The higher the value, the more color is imprinted and the stronger the contrast between the glow and the background. Valid values are 0 to 255. The larger the value, the stronger the imprint. A value of 0 means the filter is not applied. The default value is 1. |
|
quality:Number [optional] — The number of times to apply the filter. Valid values are 0 to 15. The default value is 1, which is equivalent to low quality. A value of 2 is medium quality, and a value of 3 is high quality. |
|
type:String [optional] — The placement of the filter effect. Possible values are:
The default value is |
|
knockout:Boolean [optional] — Specifies whether the object has a knockout effect. A knockout effect makes the object's fill transparent and reveals the background color of the document. The value true specifies a knockout effect; the default is false (no knockout effect). |
import flash.filters.GradientGlowFilter;
var art:MovieClip = createRectangle(100, 100, 0x003366, "gradientGlowFilterExample");
var distance:Number = 0;
var angleInDegrees:Number = 45;
var colors:Array = [0xFFFFFF, 0xFF0000, 0xFFFF00, 0x00CCFF];
var alphas:Array = [0, 1, 1, 1];
var ratios:Array = [0, 63, 126, 255];
var blurX:Number = 50;
var blurY:Number = 50;
var strength:Number = 2.5;
var quality:Number = 3;
var type:String = "outer";
var knockout:Boolean = false;
var filter:GradientGlowFilter = new GradientGlowFilter(distance,
angleInDegrees,
colors,
alphas,
ratios,
blurX,
blurY,
strength,
quality,
type,
knockout);
var filterArray:Array = new Array();
filterArray.push(filter);
art.filters = filterArray;
function createRectangle(w:Number, h:Number, bgColor:Number, name:String):MovieClip {
var mc:MovieClip = this.createEmptyMovieClip(name, this.getNextHighestDepth());
mc.beginFill(bgColor);
mc.lineTo(w, 0);
mc.lineTo(w, h);
mc.lineTo(0, h);
mc.lineTo(0, 0);
mc._x = 20;
mc._y = 20;
return mc;
}
| Method Detail |
public clone() : GradientGlowFilter
| Player version: | Flash Player 8 |
GradientGlowFilter —
A new GradientGlowFilter instance with all the same properties as the original GradientGlowFilter instance.
|
filter_1 is created by using the GradientGlowFilter construtor; filter_2 is created by setting it equal to filter_1; and, clonedFilter is created by cloning filter_1. Notice that although filter_2 evaluates as being equal to filter_1, clonedFilter, even though it contains the same values as filter_1, does not.
import flash.filters.GradientGlowFilter;
var colors:Array = [0xFFFFFF, 0xFF0000, 0xFFFF00, 0x00CCFF];
var alphas:Array = [0, 1, 1, 1];
var ratios:Array = [0, 63, 126, 255];
var filter_1:GradientGlowFilter = new GradientGlowFilter(0, 45, colors, alphas, ratios, 55, 55, 2.5, 2, "outer", false);
var filter_2:GradientGlowFilter = filter_1;
var clonedFilter:GradientGlowFilter = filter_1.clone();
trace(filter_1 == filter_2); // true
trace(filter_1 == clonedFilter); // false
for(var i in filter_1) {
trace(">> " + i + ": " + filter_1[i]);
// >> clone: [type Function]
// >> type: outer
// >> knockout: false
// >> strength: 2.5
// >> quality: 2
// >> blurY: 55
// >> blurX: 55
// >> ratios: 0,63,126,255
// >> alphas: 0,1,1,1
// >> colors: 16777215,16711680,16776960,52479
// >> angle: 45
// >> distance: 0
}
for(var i in clonedFilter) {
trace(">> " + i + ": " + clonedFilter[i]);
// >> clone: [type Function]
// >> type: outer
// >> knockout: false
// >> strength: 2.5
// >> quality: 2
// >> blurY: 55
// >> blurX: 55
// >> ratios: 0,63,126,255
// >> alphas: 0,1,1,1
// >> colors: 16777215,16711680,16776960,52479
// >> angle: 45
// >> distance: 0
}
filter_1, filter_2, and clonedFilter, the following example below modifies the knockout property of filter_1. Modifying knockout demonstrates that the clone() method creates a new instance based on the values of filter_1 instead of pointing to them in reference. import flash.filters.GradientGlowFilter; var colors:Array = [0xFFFFFF, 0xFF0000, 0xFFFF00, 0x00CCFF]; var alphas:Array = [0, 1, 1, 1]; var ratios:Array = [0, 63, 126, 255]; var filter_1:GradientGlowFilter = new GradientGlowFilter(0, 45, colors, alphas, ratios, 55, 55, 2.5, 2, "outer", false); var filter_2:GradientGlowFilter = filter_1; var clonedFilter:GradientGlowFilter = filter_1.clone(); trace(filter_1.knockout); // false trace(filter_2.knockout); // false trace(clonedFilter.knockout); // false filter_1.knockout = true; trace(filter_1.knockout); // true trace(filter_2.knockout); // true trace(clonedFilter.knockout); // false
| Properties | Methods |